Posted By: Pankaj Patel
Basics: Cell Biology & Oncology
Structure and function of cell
Consist of
- Cell membrane (Separates; Contact Inhibition)
- Nucleus (Control Centre/Brain)
- Mitochondria (Power house/energy)
- Golgi complex: Packaging & Excretory function
- Endoplasmic reticulum: Protein synthesis, excretory function
- Microtubules: formation of mitotic spindle

Nucleus & DNA
- The nucleus contains the genetic material of the cell, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
- Cell function is controlled by the genes in DNA
- DNA is Composed of Nucleotides. Each Nucleotide made of Pentose sugar, Phosphate groups & Nitrogen base (Purines & Pyrimidines)
- Adenine (A) - Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) - Guanine (G); RNA has Uracil (U) instead of (T)
- Base pairing is always the same; A=T & C≡G
DNA Synthesis/Protein Synthesis
Mitosis
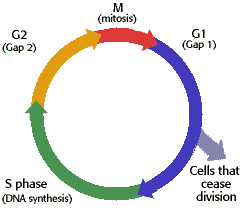
Cell Cycle

Apoptosis & Mutation
Genes In Cancer
Oncogene: A gene with the potential to cause cancer.
Eg: HER-2 neu gene (Human epidermal growth factor) in breast ca
- Proto-oncogene is a normal gene that can become an oncogene due to mutations or increased expression.
- Mutated proto-oncogenes can become carcinogenic oncogenes and can promote uncontrolled cell division(cancer).
- Tumour suppressor genes: These genes contribute to carcinogenesis when they are inactivated by mutation and can no longer provide a brake on cell division. Eg: pRb and p53
Chemotherapeutic Agents Act In Different Phases Of The Cell Cycle
Cancer
- Cancer refers to a group of different diseases that are characterized by DNA damage that causes abnormal cell growth & development.
- As a result an extra mass of tissue is formed, this is called a growth or tumor. This tumour can be benign or malignant.

Causes of Cancer
1. Environmental factors 2. Life Style
Food additives Tobacco
Pollution Alcohol
Occupation Diet
Industrial Sexual Behavior
Pollution Alcohol
Occupation Diet
Industrial Sexual Behavior
3. Infection
4. Genetic
5. Unknown
Types of Cancer
- Carcinomas (derived from Epithelial Cells)
- Sarcomas (derived from Connective tissue)
- Leukemias, Lymphomas , Myelomas (derived from Blood & Bone marrow)
- Mesotheliomas (derived from mesothelial cells lining the peritoneum & the pleura)
- Glioma (derived from glia, most common type of Brain cell)
- Germinomas (derived from germ cells, normally found in testes & ovary)
- Choriocarcinomas (derived from placenta)
Tumor Node Metastasis (TNM staging)
- TX: Primary tumor cannot be assessed
- T0: No evidence of primary tumor
- Tis: Carcinoma in situ
- T1 – T4: increasing size and/or local extent of the primary tumor
- NX: Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
- N0: No regional node metastasis
- N1 – N3: Increasing involvement of regional lymph nodes
- M0: No evidence of metastatic spread
- M1: Evidence of metastatic spread
Types Of Cancer Therapy
- Surgery: It involves removal or resection of tumor mass surgically
- Radiation therapy: It involves application of X-rays or Gamma rays to a tumor site, mostly in solid tumor.
- Chemotherapy: It involves administration of chemotherapeutic agents systemically or by regional perfusion
- Immunotherapy (Biotherapy): It involves administration of biological response modifiers systemically. Eg: interferon
- Hormone therapy: hormone therapy involves blocking of particular hormone receptors to impede the progression of cancer. Eg: Leuprolide in prostate cancer.
Classification Of Chemotherapeutic/Anti-cancer Drugs
- Alkylating Agents (Nitrogen Mustards; Cyclophosphamide & Ifofsamide; Chlorambucil; Melphalan; Alkyl-Sulfonate: Busulfan; Nitrosoureas: Carmustine (BCNU), Lomustine (CCNU); Triazine: DTIC (Dacarbazine))
- Antimetabolites (Folate antagonists: Methotrexate (Mtx), Purine Antagonist: 6 Mercaptopurine (6 MP), 6 Thioguanine (6 TG), Azathioprine, Pyrimidine Antagonist: 5 Fluorouracil (5FU), Cytarabine)
- Vinca alkaloids (Vincristine, Vinblastine)
- Taxanes (Paclitaxel, Docetaxel)
- Epidophyllotoxin (Etoposide)
- Campothecan Analogues: (Topotecan, Irinotecan)
- Antibiotics (Actinomycin D, Doxorubicin, Daunorubicin, Mitoxantrone, Bleomycin, Mitomycin, Mithramycin)
- Miscellaneous (Hydroxyurea, Procarbazine, L Asparaginase, Cisplatin, Carboplatin)
Great information. This works great for me. Thanks for sharing this :)
ReplyDeleteTechOverFly consistently delivers relevant, high-quality news that covers business, politics, and technology comprehensively. Its emphasis on trends, policy changes, and industry shifts ensures readers remain well-informed and empowered to make intelligent decisions.
ReplyDeleteFoxNewsPaper delivers more than just headlines—it provides context, analysis, and thoughtful insights on current events. The platform’s dedication to accuracy and timeliness ensures readers receive reliable information that helps them understand and navigate today’s complex world.
ReplyDeleteNewsFeedInfo provides news with precision and depth, offering more than just headlines. The platform’s focus on insightful reporting and thorough analysis ensures that every reader gains a clear understanding of global events as they unfold, consistently delivering valuable content.
ReplyDelete